ICSI – Know Its Purpose, Process, and Risks
Whenever couples face conception issues, they visit one of the best fertility or ICSI clinics in India to see a fertility specialist. After interacting with the couples, knowing their medical history, and going through the reports of a few recommended tests, the specialist recommends a few fertility treatment options. And ICSI is one of those recommended options. Here, know its purpose, process, and risks.
ICSI – what it is
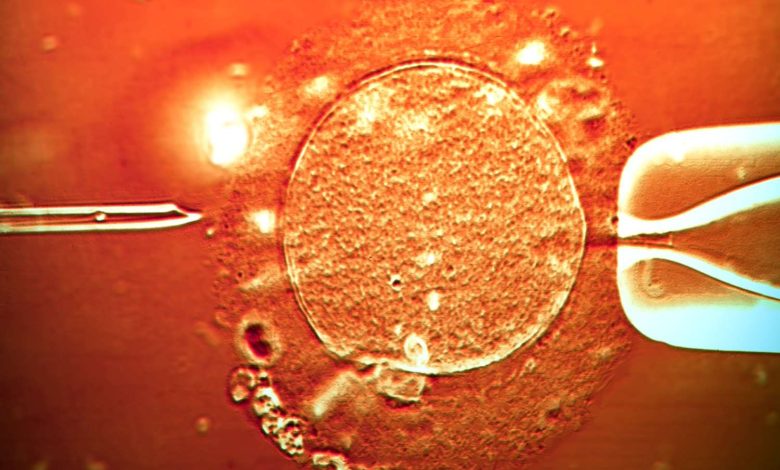
ICSI stands for Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection, which is a form of assisted reproductive technology (ART) used to help couples conceive when male infertility is a factor. During the ICSI treatment, a single sperm is directly injected into an egg using a tiny needle under a microscope. The fertilised egg (embryo) is then transferred to the woman’s uterus or frozen for later use.
Why Does A Doctor Recommend ICSI?
A doctor may recommend ICSI (intracytoplasmic sperm injection) as a form of assisted reproductive technology (ART) when there are male factor infertility issues that make it difficult for sperm to naturally fertilise the egg. ICSI is typically recommended when the male partner has:
- Low sperm count: If the concentration of sperm in the semen is too low, it can be challenging for the sperm to reach and fertilise the egg.
- Poor sperm motility: Sperm with poor motility (ability to move) may not be able to swim to the egg and fertilise it.
- Abnormal sperm morphology: If the shape or size of the sperm is abnormal, it can make it difficult for the sperm to penetrate the egg.
- Obstructive azoospermia: A blockage in the male reproductive tract can prevent sperm from reaching the semen and being ejaculated.
- Non-obstructive azoospermia: In some cases, there may be a complete absence of sperm in the semen due to a problem with sperm production.
ICSI can also be recommended if a previous attempt at in vitro fertilisation (IVF) has failed or if the couple is using frozen sperm.
ICSI Treatment Process
The ICSI treatment process generally involves the following steps:
- Ovarian Stimulation: The woman is given medication to stimulate the ovaries to produce multiple eggs.
- Egg Retrieval: The eggs are retrieved from the woman’s ovaries using a needle under ultrasound guidance.
- Sperm Collection: The male partner provides a semen sample, which is prepared in the laboratory to obtain the healthiest and most motile sperm.
- Sperm Injection: A single sperm is injected directly into each mature egg using a fine needle and a powerful microscope.
- Fertilisation: After injection, the fertilisation is checked the next day to see if the egg has been successfully fertilised.
- Embryo Culture: Fertilised eggs are cultured in a laboratory for several days to develop into embryos.
- Embryo Transfer: One or more embryos are transferred to the woman’s uterus, usually 2-5 days after fertilisation. Any extra embryos may be frozen for future use.
- Pregnancy Test: About two weeks after the embryo transfer, a pregnancy test is performed to determine if the treatment was successful.
It is essential to work closely with a qualified and experienced fertility specialist who can guide you through each step of the ICSI process and provide you with the best chance of success.
Suggest To Read – What Is The IVF Treatment Procedure?
ICSI Treatment Risks
ICSI (intracytoplasmic sperm injection) is a specialised and effective form of assisted reproductive technology (ART) used to treat male infertility. However, like any medical procedure, there are potential risks and complications associated with ICSI. Some of the risks of ICSI treatment include:
- Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS): This is a potential side effect of the medications used to stimulate the ovaries to produce multiple eggs. OHSS can cause abdominal pain, bloating, nausea, and in severe cases, fluid buildup in the lungs or abdomen.
- Bleeding and infection: There is a small risk of bleeding and infection during the egg retrieval procedure.
- Multiple pregnancies: If more than one embryo is transferred to the uterus, there is a risk of a multiple pregnancy, which can increase the risk of complications for both the mother and babies.
- Ectopic pregnancy: In rare cases, the embryo may implant outside the uterus, which can be life-threatening.
- Birth defects: While the risk is small, some studies suggest that children born through ICSI may be at a slightly higher risk of certain birth defects, such as heart defects and urogenital abnormalities.
- Emotional and financial burden: The emotional and financial burden of infertility treatment can be significant, and may cause stress, anxiety, and depression.
It is essential to discuss the potential risks and benefits of ICSI treatment with a qualified and experienced fertility specialist, who can provide you with personalised information and guidance. Your doctor will work with you to minimise the risks and increase your chances of successful conception.
Conclusion
Having an idea about fertility treatment options such as ICSI is highly beneficial. It will help you make a wise decision if you are suffering from fertility problems or conception issues.



